
Fundamentals of Financial Statements Analysis
Financial Statement analysis is carried out through methods, often defined as techniques that allow knowing the entity’s transactions on its financial situation and results.
Based on the order to follow the analysis, these methods simplify and separate the financial statements’ numerical data from measuring the relationships in one period or the changes in several accounting years.
Based on the comparison of values, vertically or horizontally, analysis methods are defined as the Vertical and Horizontal methods.
Vertical Method
The Vertical method consists of analyzing the financial information of a single year to determine the participation of each account in the Financial Statement regarding total assets or total liabilities and equity, in the case of the Statement of Financial Position, or to the total sales, in the case of the Income Statement.
|
Statement of Financial Position Example |
 |
| Income Statement Example |
 |
The Vertical method, also called static because it applies to the same year’s financial statement, establishes comparisons between the same items vertically, studies the relationships between a company’s financial elements, and shows how values invested in it are distributed.
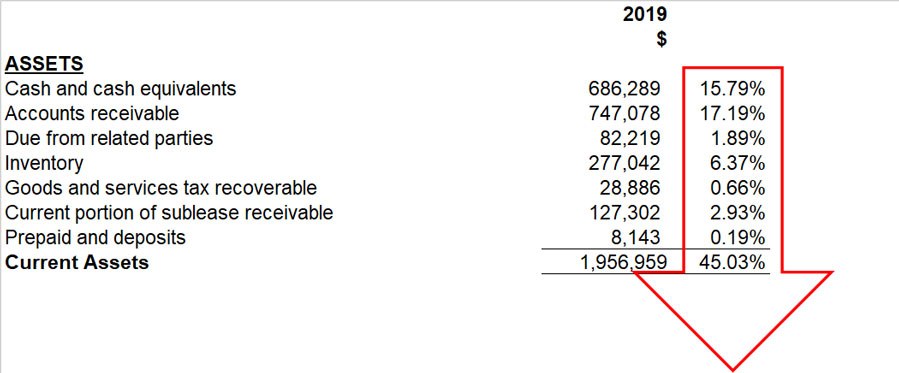 |
This method allows to know which items have predominance in the Financial statement understudy, weight the percentage of existing interrelationships between entities, and see the magnitude of importance they have within the financial information.
In the Statement of Financial Position, total assets get the value of 100%, and an account’s net value is compared to establish their proportional magnitude against the total investment. The same applies to liabilities and equities accounts, whose values compared with the total liabilities plus equity has a value of 100%. In an Income Statement, net sales get the value of 100%, and the rest of the accounts is compared against this base percentage.
Thus, this method reduces the amounts of the accounts of the same nature contained in the financial statements to percentages by dividing each one by the general group’s total to which they correspond. This procedure allows determining the weight of a particular account, indicating to the analyst in which accounts weaknesses, deviations, and abnormalities are observed to take corrective measures.
Horizontal Method
The horizontal method of analizing financial statements consists of comparing several years of financial statements, item by item, in a horizontal correlative manner.
Several successive years are usually studied; generally, at least the last year’s financial statements and the immediately previous year are included. A comparative examination between the two allows identifying the evolution of the different items.
The horizontal method can be understood as a dynamic analysis technique that deals with each account’s changes or movements between one period and another. This method relates the financial modifications suffered by the company, and its represented in increases and decreases, or even percentages, allowing a good view of obtaining the changes.
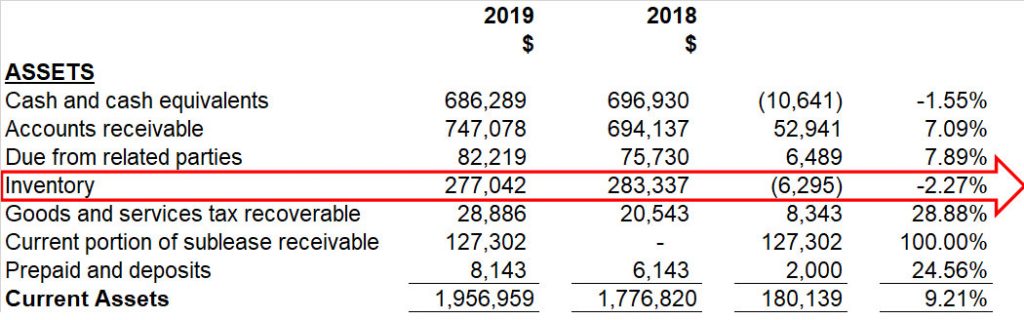 |
Analyzing increases and decreases consists of comparing homogeneous concepts of financial statements on at least two different dates locating the differences, and analyzing the figures’ behaviors from one period to another. The variation, positively or negatively, from one period to another is determined.
With these methods, business owners, banks, and others interested in understanding the financial statements can identify the variations that have occurred in the accounts in an obvious way and later determine the degree of impact on any company’s economic situation, be it small or medium.
Written by: Andrea Diaz
Related Articles:
Newsletters
e-Newsletter – June 2018
NewslettersEvents & SponsorshipArticles & Publications
e-Newsletter – May 2018
NewslettersEvents & SponsorshipArticles & Publications
e-Newsletter – April 2018
NewslettersEvents & SponsorshipArticles & Publications
e-Newsletter – March 2018
NewslettersEvents & SponsorshipArticles & Publications
e-Newsletter – February 2018
NewslettersEvents & SponsorshipArticles & Publications
Events & Sponsorship
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Articles & Publications
Is Cryptocurrency Taxable in Canada?
Is cryptocurrency taxable in Canada? According to CRA, possessing or holding a cryptocurrency is not taxable. However, selling, making a gift, trading or exchanging a cryptocurrency, including disposing of one to get another, or converting cryptocurrency to a...
Have Unfiled Tax Returns For Years?
Do You Have Unfiled Tax Returns For Years? As for the record, the CRA wants you to file and pay your taxes on time every year. When you cannot do so, you may put yourself at risk of high penalty amounts and collection tasks like bank levies or wage garnishments. We at...
Old Age Security One-Time Payment Only
Old Age Security One-Time Payment Only. You will receive the one-time payment for older seniors if you were: born on or before June 30, 1947, and eligible for the Old Age Security pension in June 2021 If you have applied for the Old Age Security pension but have not...
CRA Notice of Objection
CRA Notice of Objection (NOO) Once you file your taxes, you receive a Notice of Assessment and later a Notice of Reassessment. You have two options: Pay the taxes owing File a CRA Notice of Objection (NOO). The CRA is not always right; when you disagree, you can...
All You Need to Know About Trust Funds in Canada
All You Need to Know About Trust Funds in Canada A trust is a vehicle for holding and passing on the family property. As such, it typically serves at least one of two purposes: It can reduce a family's taxes by shifting income to members in lower tax brackets, and it...